FAQS
What is a Gas Heater and How Does It Work?
Gas heaters are an effective way to warm your home during colder months. They operate using natural gas or propane, converting fuel into heat. This process occurs in a combustion chamber, where gas ignites and produces warmth.
Many people enjoy the quick heating power of gas heaters. They are often more efficient than electric options, providing rapid temperature increases. However, safety must always be a priority. Improper ventilation can lead to dangerous gas buildup. Regular maintenance is essential to ensure efficiency and safety.
Despite their advantages, gas heaters require careful consideration. The initial installation can be costly, and not every home is suited to them. Additionally, gas prices can fluctuate, affecting long-term expenses. Understanding these factors can help in making informed decisions. Always reflect on your heating needs before choosing gas heaters.

What is a Gas Heater: Definition and Overview
A gas heater is a device that uses gas, typically natural gas or propane, to generate heat. It converts gas into warmth through combustion. This process involves burning the fuel to produce hot air, which then circulates into your home. Gas heaters come in various types, including wall-mounted units, central heating systems, and portable models. They offer an efficient way to heat spaces quickly.
The operation of a gas heater starts with the ignition of the gas. A pilot light or electronic ignition sparks the gas, creating a flame. This flame heats up metal exchangers. The warm air then blows into living areas. But users must be cautious of gas leaks. Proper installation and maintenance are crucial. If neglected, it can lead to dangerous situations, such as carbon monoxide buildup. Regular checking is necessary for safe use.
While gas heaters are usually efficient, they are not without their drawbacks. They require proper venting to ensure safety. Some users may find them less energy-efficient in poorly insulated homes. Ensuring a good connection to the gas supply is essential. If connections are loose, it can cause problems. These factors remind us of the importance of understanding how to operate gas heaters safely.
Types of Gas Heaters: Variations and Applications
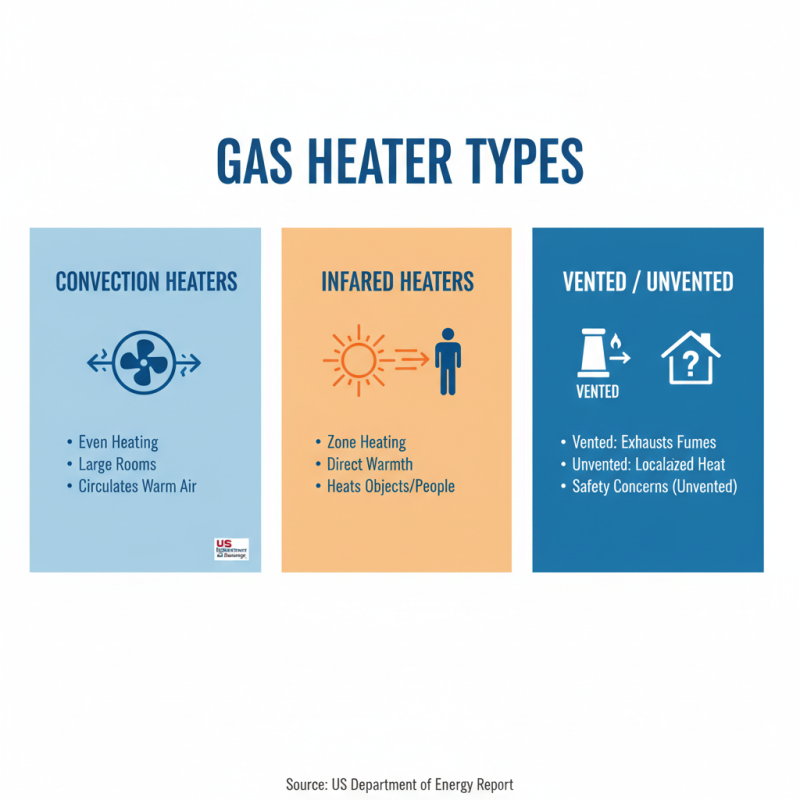
Gas heaters come in various types, serving different purposes in residential and commercial spaces. The most common types include convection heaters, infrared heaters, and vented/unvented systems. According to a recent report by the U.S. Department of Energy, convection heaters are known for even heating, making them ideal for larger rooms. Their ability to circulate warm air can significantly improve comfort in cold climates.
Infrared heaters, on the other hand, provide instant warmth by emitting infrared radiation. This method is highly efficient, yet it may not warm up entire spaces evenly. They are often used in patios or workshops where quick heat is required. Interestingly, some studies suggest that nearly 75% of users prefer infrared models for their lower operational costs over time.
Vented gas heaters are connected to a flue, expelling exhaust gases outside. This can lead to greater efficiency, but improper installation can pose safety risks. Unvented models, while easier to install, can lead to indoor air quality issues. Users should critically evaluate their needs before choosing a system. Many homeowners underestimate these factors, leading to regret later. Effective use of gas heaters requires awareness of both benefits and potential drawbacks.
Key Components of a Gas Heater and Their Functions
Gas heaters are popular for their efficiency and warmth. Understanding their components can help users maintain them effectively.
One key component is the burner. It ignites gas to create heat. A pilot light or an electronic ignition system often starts the process. The heat exchanger is vital as it transfers heat from the burning gas to the air. Air travels through ducts and warms up living spaces. Sometimes, the heat exchanger may develop cracks, potentially causing safety risks.
Another important part is the thermostat. It regulates temperature by controlling the heater's operation. If the thermostat fails, the heater may overheat or underperform. Additionally, gas supply lines play a crucial role. They deliver gas from the source to the burner. Any leaks in these lines can lead to dangerous situations. Regular checks are essential to ensure everything functions well. Each component works together, but flaws can occur unexpectedly. Understanding these parts aids in troubleshooting.
How Gas Heaters Work: The Heating Process Explained
Gas heaters operate by utilizing natural gas or propane to generate heat. The process begins with the ignition of gas in a burner. This creates a flame that heats a heat exchanger. The heat exchanger then warms the air or water circulating through your home. The warm air is distributed through ducts or vents. If water is used, it travels through pipes to radiators or underfloor heating.
During operation, gas heaters require proper ventilation. Combustion generates byproducts that must be vented outside. Without adequate ventilation, carbon monoxide can accumulate, posing safety risks. Regular maintenance is necessary to ensure the system runs efficiently. Dirty burners can lead to incomplete combustion, reducing heat output.
When considering gas heaters, energy efficiency is essential. Older models may consume more gas than newer ones. This can lead to higher utility bills. Always check for leaks and ensure pilot lights are functioning properly. Ignoring these details can lead to costly repairs or safety hazards. The heating process is effective but requires attention to detail.
What is a Gas Heater and How Does It Work?
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Type of Gas Used | Natural Gas / Propane |
| Heating Method | Combustion of Gas |
| Main Components | Burner, Heat Exchanger, Thermostat |
| Efficiency Rating | 80% to 98% (depending on the model) |
| Safety Features | Oxygen Depletion Sensor, Automatic Shutoff |
| Common Applications | Residential Heating, Water Heating, Industrial Heating |
| Installation Considerations | Ventilation, Gas Line Access, Space Requirements |
Safety Measures and Maintenance for Gas Heaters
Gas heaters provide efficient warmth, but they come with risks. Safety measures are essential for every user. For instance, the National Fire Protection Association reports that heating equipment is involved in 56% of home fires. Regular maintenance can reduce these risks significantly.
One critical step is ensuring proper ventilation. Poor ventilation can lead to a buildup of harmful gases. Carbon monoxide detectors should be installed in every home with a gas heater. These devices can save lives. Regular inspections, ideally every year, can help identify leaks and other dangers.
Cleaning the heater is also vital. Dust and debris can accumulate, affecting performance. Experts recommend cleaning the heater’s components regularly. Ignoring maintenance tasks may lead to inefficiency. This not only increases energy costs but can also pose serious safety threats. Making safety a priority ensures a warm, secure environment.
Related Posts
-

How to Choose the Right Commercial Electric Heaters for Your Business Needs
-

How to Choose the Best Infrared Panels for Your Home Heating Needs
-

Top 10 Electric Heaters for House Efficient Heating Solutions You Can Trust
-

2025 Top 5 Wall Mounted Heaters: Efficient Heating Solutions for Every Home
-

10 Best Natural Gas Patio Heaters for Ultimate Outdoor Comfort in 2023
-
Top 10 Tips for Using an Electric Space Heater Efficiently and Safely
 Skip to content
Skip to content
